11 Steps to Write Effective Business Reports
The transition from academic writing, such as essays and articles to sophisticated report writing and business report, can be frightening!
Almost every line of work requires some sort of business report. These documents, which are based on facts, are utilized by businesses to make decisions.
You can utilize business report for a variety of things, including pitching, assessing, and showing that your firm conforms with social and legal requirements, as well as any specialized topic linked to your career and area of work. Therefore, it is imperative that you comprehend the notion of business report and know how to create them successfully. This article will discuss the many report types, their functions, and the significance of business.
What is a Business Report?
An official document that includes factual information, statistical data, research findings, or any other type of material pertinent to the duties of the position is referred to as a business report.
This report is a formal document that is short and to the point in order to convey information. Business reports are mostly utilized within a business for internal communication.
A key component of producing business reports is objectivity. Everything you say should be backed up by data and facts, not assumptions and viewpoints. For instance, you might use facts to demonstrate “sales in the last quarter were quite low” rather than simply stating it.
Also Read: What Is Business Financial Statements
Types Of Business Reports
An organization may employ a variety of business reports for a number of reasons. It goes without saying that you cannot compare employee performance and sales for the previous quarter using the same report.
Article you might find interesting: Top Barcode Scanners for Inventory Management In 2022
Here are a few typical business report formats:
- Informational reports
- Analytical Report
- Research Report
- Explanatory Report
- Progress Report
Informational reports
When your boss requests entirely objective information that is, facts without any justification or possible outcome you use this report. For instance, a report on the company’s workforce listing the number of employees, their job titles, the departments they work in, and their responsibilities
Analytical Report
As the name implies, this report is used when it’s necessary to study certain important business facts to make wise judgments.
Analyzing the decline in sales from the previous fiscal year, for instance. This study includes sales figures, a comparison of those figures to previous years, and an analysis of the causes behind the decline. The report will also outline potential steps the business can take to address this issue.
Research Report
When there is a major event approaching, you employ a study report! It can involve a potential merger, a new product line, or a change in the way things are done now.
A thorough analysis of all the effects of a significant change is required. For instance, the research report will include factors like target audience, marketing communication strategy, advertising campaigns, etc. if the company intends to launch a new product.
Explanatory Report
When you want the team to understand your project, you use this report. Let’s say you did some research.
The data, the results, and the research’s conclusion will all be presented in an explanation report. It must be written in straightforward, succinct language. Jargon should be avoided even though the readers are primarily other professionals in the same field.
Progress Report
This brief report is intended to inform employees about company updates.
- How did last week go?
- How are things doing with the sale for this quarter?
- What percentage of conversions have changed since the previous week/month?
A progress report provides the answers to inquiries like these. There is no analytics present. only updates and modifications.
Progress reports are a useful tool for businesses to keep track of their ongoing tasks and generate fresh suggestions for development and progress.
The Importance of Business Reports
- Mode Of Communication
- Decision Making
- Crisis Management
- Effective Management
1. Mode Of Communication
Do you text or call people in your daily life to communicate? Reports are created for it in businesses. Business reports serve as a channel of communication within a corporation, so to speak.
However, why is it done?
Well, there is a whole line of workflow that occurs in large businesses. It also goes by the name “delegation of duty.” There are branches, sub-branches, divisions, and zones tailored to particular niches in this workflow. Verbal communication increases the risk of knowledge loss and contamination.
2. Decision Making
Considering introducing a new product line? Construct a report.
Trying to lower business expenses? Construct a report. Every choice, from choosing the target market to firing personnel, is based on thorough reports generated with facts and figures.
In an organization, reports are shared in both directions. Business reports are written by employees and sent to top management for decision-making. Reports are written by upper management and distributed to the workforce to communicate information, tasks, etc.
3. Crisis Management
Everyone has an opinion on the subject when there is a crisis, commotion, or panic attack, and the verbal exchange of ideas leads to office gossip.
Business reports are made in this case to get everyone on the same page and then factually assess the issue.
The root of the problem, procedures to be taken for damage control, and policies proposing future crisis protection are all included in crisis management reports.
4. Effective Management
Through reports, duties are assigned. Each employee has a list of personal chores with a due date. This aids in the company’s management becoming sounder and more efficient.
Business reports improve the overall running of the organization, contain all the necessary information, and allow choices to be made after thorough consideration.
Now that we are aware of the necessity of producing business reports to succeed in the corporate world, let’s move on to the following and arguably most crucial section where we show you how to begin writing an appropriate report.
Article you might find interesting: How IoT for Small Businesses Can be More Efficient
How To Write a Business Report?
To Develop Your Effective Business Report, Follow The 11 Steps Below:
- Create a plan of action
- Check for an in-house format
- Add a title
- Write a table of contents
- Add a Summary/ Abstract
- Write an introduction
- State your methodology
- Present your findings
- Give a conclusion or recommendation
- Add a bibliography and references
- Proofread
Step 1: Create a plan of action
Not an essay for class, but a business report. Your report cannot be based solely on your current state of mind. Determine the report’s purpose before you begin.
Specify the report’s objectives and the format you intend to use for presenting it. Avoid avoiding the issue! This will assist you in producing a clear and succinct report.
Step 2: Check for an in-house format
Report writing may follow a certain format at your company. To locate it, speak with your manager or look in the manual for the business. Do not rely just on the internet.
In contrast, you can use the default global format listed in the subsequent steps if no such format is specified.
Step 3: Add a title
The brief you received from your supervisor may include a description of the report’s title. You may create your title if you don’t. It must be concise, straightforward, and able to communicate the report’s goal.
You should refrain from utilizing lengthy and intricate titles. Instead of writing “Analyzing the consumer engagement with the company in the last 12 months in comparison to previous years,” use “Sales report for FY 2020-21.” When you begin your report, people will snore and walk out of the room.
Include your name as well as the names of anyone else who contributed to the report. It is highly unethical to present the hard work of another as your own in the workplace.
Step 4: Write a table of contents
A table of contents page should only be used if the report is lengthy and has sub-sections.
If this page is added, be sure to format the information precisely how the report’s headings are written. For the reader to easily navigate the report or jump to a specific section, all the contents should be properly numbered.
Step 5: Add a Summary/ Abstract
In any report, this page is crucial. The abstract should be written in such a way that, even if a reader does not read the complete report, this page can still provide them with a thorough understanding of everything.
Your title, issue, main findings, and conclusions should all be included. To fit in the abstract, you should essentially summarize everything you wrote in the report.
Step 6: Write an introduction
Your report proper is now underway. Include a summary of the main argument and the report’s purpose on this page.
On this page, you can also provide some context for the subject.
Step 7: State your methodology
Tell the readers how you produced this report on this page. It covers information sources, data types (qualitative or quantitative), information delivery channels, etc.
This is done to give your readers a better understanding of the steps you took, or, to use urban slang, the BTS of the report. Your report gains credibility as a result.
Step 8: Present your findings
Your findings are presented in this part, which is the major one. It should demonstrate that you did an extensive investigation. Include statistics, figures, and graphs to illustrate your points.
Align the material into several headings and subheadings to keep it from becoming disorganized. When necessary, use points, bulleted lists, or numbers.
Step 9: Give a conclusion or recommendation
Your paper should have a strong conclusion. This conclusion should be based on the earlier findings.
Additionally, you can make suggestions for a policy’s modification or enhancement, backed up by credible evidence. The conclusion ought to be compelling and supported by factual information rather than prejudicial viewpoints or opinions.
Step 10: Add bibliography and references
Any report that uses information from previously published source whether directly or indirectly is required by law to include this section.
Let’s give a little explanation. You must give proper credit to the original author if you have added any data or statistics to your report. If not, it constitutes plagiarism, a punishable crime.
Additionally, keep in mind the distinction between references and bibliography, and avoid mixing the two!
Here’s an example:
Let’s say you were motivated after reading a business report online. But you didn’t include any of its information in your report. In this case, you would include a list of that report in the bibliography.
If, however, you directly incorporated information from that report into your own, you must note that in the reference section.
Step 11: Proofread
Before submitting a paper for review, proofreading or revision are crucial. Verify this section for any typographical, grammatical, or punctuation problems. These minor errors can leave a lasting negative impression.
Check the citations, footnotes, appendices, etc. during proofreading as well, making sure they adhere to the firm standards. There might be rules you overlooked while composing the report.
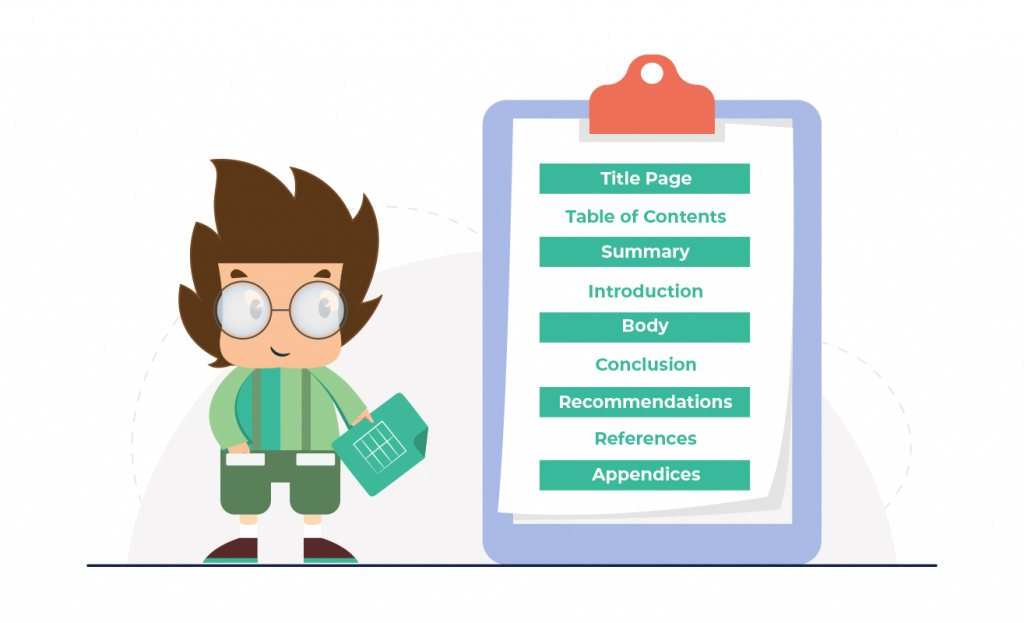
Components of a Business Report
Title Page
Table of Contents: You might want to think about providing a table of contents depending on how long the report is. Readers will find it simpler to find specific information as a result.
Summary: This section, which typically ranges in length from a few sentences to a paragraph, includes a succinct summary of the report’s main points. The key points from each section of the report would be clear to anyone who read this section.
Tip: Even though this is the first section, you might want to write it once the report is complete. This will enable you to decide which issues need to be addressed the most.
Introduction: What you will cover in your report is outlined in this section. It contains your report’s main points, preferred report structure, and most importantly its goal.
Body: You should go into more depth about each of your report’s topics in the body. The titles in this section let your reader know what details are in the paragraph(s) that follow. Depending on the type of report, the information or data you are providing to the organization, and whether or not a comprehensive analysis is required, the structure of this part will change.
Examples of headings:
– Methods
– Findings
– Research
– Analysis
– Graphs
Conclusion: Make sure to quickly recap all of the major points in the report in the order they were discussed in the conclusion.
Recommendations: based on the conclusions, you noted in earlier sections, make any recommendations or suggestions in this section. Indicate the potential advantages of implementing your recommendations for the company.
References: Make sure this section of the report includes citations for all sources used.
Appendices: In the appendix, you can include pertinent reports, polls, graphs, and other materials that you referred to in the report
Wrap Up
As we’ve seen, there are several factors to consider while producing a business report. One spends all of their time and effort on interesting material, often neglecting the design aspect. Yes, any report’s design is a crucial component. A visually appealing report draws the reader in and stands out in a sea of monochromatic text.





Recent Comments