Stock Keeping Unit (SKU)
Retail
Stock-keeping units are widely used by retail stores, factories, warehouses, eCommerce vendors, service providers, and product fulfillment centers for purposes of inventory tracking and sales.
Let us see what is the stock keeping unit. and why it is important.
What Is A Stock Keeping Unit (SKU)?
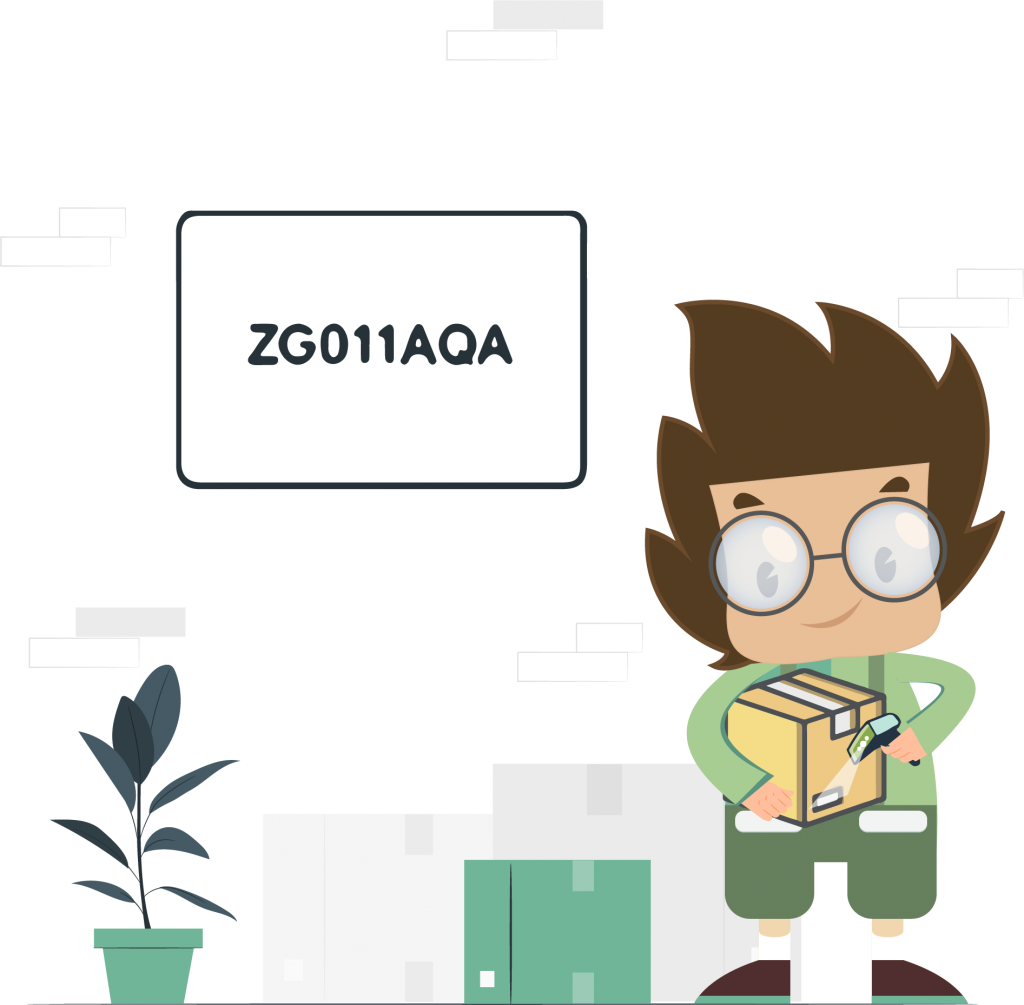
SKU stands for “Stock Keeping Unit”, pronounced “skew”, which is a product or service identification code. In other words, it is a unique code for all your products consisting of alphanumeric combinations and may include a scannable bar code that allows tracking the inventory movement and ease of inventory management. This helps sellers to identify and track the products in their warehouse.
The Importance Of Stock Keeping Units
The importance of stock keeping unit is that it is essential as a product’s ID card, it has many uses beyond identifying a specific product, or tracking inventory.
It is a main part of information for each product that allow retailers to classify or identify each product by its details such as color, price, size, style, manufacturer, brand, etc.
This information, when collected, can be analyzed to determine which goods are the most profitable and measure the efficiency of your retail business.
Besides, SKUs help to Identify inventory shrinkage, track your inventory accurately to define when to order new products (the reorder point for products) in order to prevent inventory stock out.
On top of this, retailers use SKUs to enhance shopping experiences and help shoppers save time by allowing them to find products quickly and compare characteristics of similar items.
Businesses create different codes of SKUs for its products and services based on their important criteria.
The data in SKUs should include only the most necessary data, and be sorted from most to least important.
How To Create SKU Codes?
Each company utilizes its own method of creating SKUs for its products. However, there is no incorrect way of creating an SKU, but there are some standards with best practices while constructing an SKU for a product.
While you can also create SKUs by hand, but the simplest and easiest way to generate SKU codes is through your inventory management system or your point-of-sale (POS) system, especially for companies with large inventories.
When you start to generate SKU units for your products, SKU architecture should be relevant to your brand needs, sales priorities and customer favorites.
So how can you design a correct SKU architecture?
In the first place, you have to determine what information will be used to encode in its numbers and letters, so you can easily generate new SKU for each new product.
Another step to do is to organize volume of inventory as the volume of stock in your company influences also the way of generating SKUs.
The right SKUs for your products should represent your product information priorities.
Since the main purpose of SKU is to identify products from each other, It would be difficult to track inventory and sales unless you classify the products by color, model, size, type, or any other identifying traits.
A stock keeping unit consist of letters and numbers that provide the information about the product.
Commonly, the first part of an SKU is the wider characteristic, like the supplier, product category, or department. the company map the top two or three alphanumeric characteristics to this.
The next few characters represent specific features to each product, such as its color, type, size, model, brand, or other subcategory.
Lastly, the last two- or three-characters act as a sequence identifier, so your SKUs determine the number of products in your stock and the order of purchase and processing.
Tips For Your SKU Naming Convention
1- Stay between 8 and 12 characters
2- Begin the SKU with a letter, for example, the first letter of your brand or supplier.
3- Make every single SKU specific.
4- Create a unique, non-duplicated, easy-to-understand SKU number.
5- Never reuse an SKU at all, even if a product has been removed from the catalog, and make sure that a unique SKU comes for each product. Avoiding duplicated SKUs is essential for eliminating shipping errors and ensuring good tracking of inventory.
6- Keep SKUs brief and short. in some inventory management systems, Long SKUs may be difficult to read, so it may not work.
7- Never use zero, particular space, or special characters like !, @, or &, Creating such an SKU may confuse people.
8- Never use letters that may be confused for numbers, for example, do not use O and I, which can be mistaken for 0 and 1.
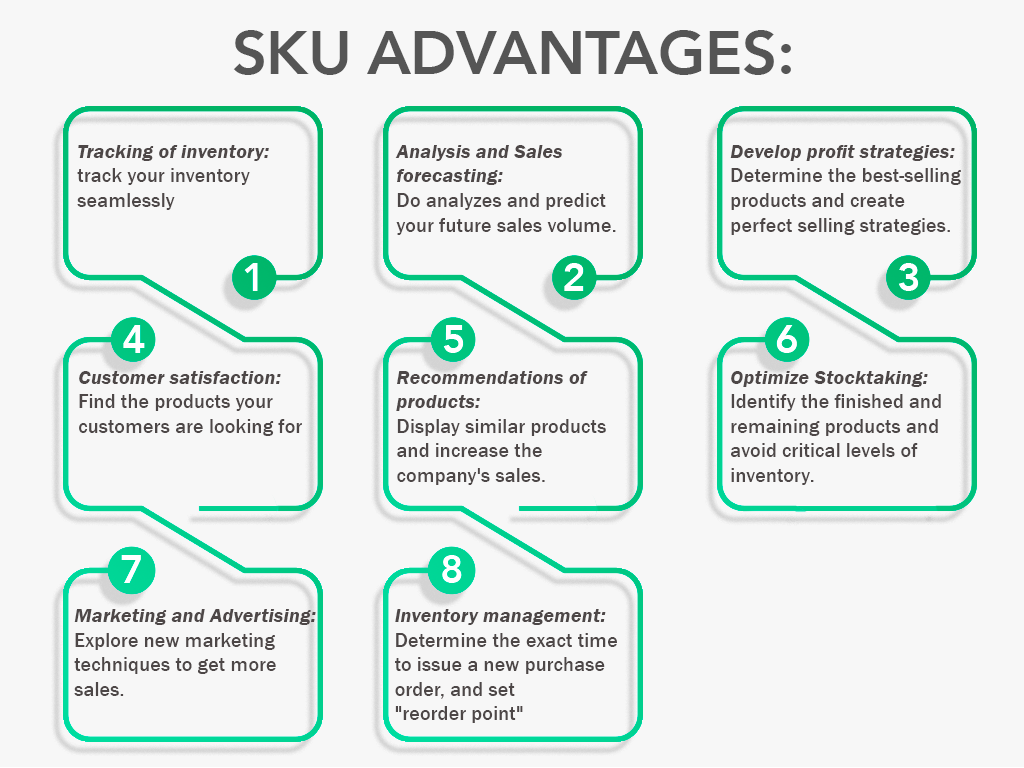
SKU Advantages
1- Tracking Of Inventory:
If your products are in the warehouse, then you need to know how many products are available, and what sizes or colors are available. Using a good SKU architecture will make it easier to locate the product associated with its related catalog data, for example, stock levels, shipments & orders, supplier information or manufacturer, and so on.
It will be easier to figure out the sales rate for each product, find many ways to move out stagnant stock, therefore, your warehouses would not accumulate nonprofitable products or reach critical levels.
In the simplest of terms, if you have an SKU, tracking your inventory will become much easier.
Follow this link to see how to create a new product with SKU:
https://newgsolution.com/userguide/documentation/warehouse/products/
2- Analysis And Sales Forecasting:
Stock keeping units (SKU) give accurate numbers about the products that you own within your warehouse. This data gives you the ability to store inventory that coincides with consumer behavior trends, analyze the volume of demand more efficiently, and predict your future sales volume.
It also enables you to identify quickly which products are performing better or worse. Thus, it allows you to know your business’s future needs, and make better decisions regarding sales and marketing witch, in turn, grow your business.
3- Develop Profit Strategies:
The stock keeping unit enables you to follow your products more easily and create detailed reports on your products to determine what is the best-selling product and vice-versa. Accordingly, you become fully aware of your major profit streams. You can then create selling strategies that can help you increase your sales and thus increase your profits.
See how to find a product by its SKU in the sales report through example:
4- Customer Satisfaction:
Thanks to the SKU, you can always help your customers to find the product they are looking for, or want an alternative version of it, make sure of its availability or lack thereof, compare product features, and display the current stock level. You can then offer alternatives in case the required product is out of stock without having to visit the warehouse.
Moreover, you can leverage more spaces at your store by reducing the exhibited stock to just one item per category. Like this, your sales efficiency and customer satisfaction would increase.
5- Recommendations Of Products:
Using SKUs allows finding a product, comparing its features, and displaying similar products as “suggestions” when you are shopping by using SKUs, which leads to additional purchases from shoppers. Consequently, this can boost customer satisfaction and increase the company’s sales and revenue.
If you have catalogs containing any number of SKU, thousands, for examples, you can leverage from software that automates each products information, such as a Product Information Manager (PIM).
6- Optimize Stocktaking:
Inventorying large quantities of inventory manually is a very difficult process, especially for small businesses.
When you add an SKU for each product you have, it makes it easier for you to determine the rate of sales for each product and identify the finished and remaining products. As a result, you will avoid the accumulation of unprofitable products and critical levels of inventory.
7- Marketing And Advertising:
Using an SKU is modern technique of advertising that makes your products unique, gives you new marketing techniques to get more sales, and makes it difficult for competitors to match product models and pricing strategies. So, it well be harder for shoppers to find the exact model at another store.
8- Inventory Management:
Using the information gathered from sales, SKU helps manage your inventory very efficiently and includes determining the exact time to issue a new purchase order, setting a “reorder point” to avoid being out of stock of the most requested products. It also determines where and how the inventory is lost and reduces the costs of inventory holding.
SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) Vs. UPC (Universal Product Codes)
Once you hear about SKU, you may ask “What’s the Difference Between SKUs and UPCs?”
Here are some differences that show you the difference:
SKU
- Alphanumeric
- Variables length: between 8 and 12 characters
- Unique for each company
- Used to identify the product information
- Usually begins with a letter
- Used to track inventory
UPC
- Numeric
- Variables length: 12 characters
- Universal
- Used to identify the product and the manufacturer information
(SKU) Stock Keeping Unit Example
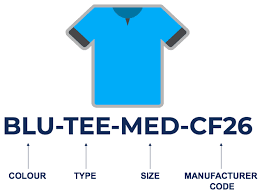
Assume we have to assign an SKU for this specific product:
“Medium-sized pair of black Gucci jeans”
For this product, we can construct an SKU as follows:
BLK-MED-G123-GUC
Here:
- To separate specific details regarding the product, a dash (-) is used.
- BLK refers to the product color that is Black.
- MED refers to the medium product size.
- G123 refers to the model number given by the producer.
- GUC relates to the brand of the product.
Know more about SKU and Master SKU in the link below:


Recent Comments