OEM And ODM Manufacturing
Retail
LAST UPDATE: NOV 13, 2022
8 minutes reading
Although many people frequently mix up the two terms OEM And ODM and use them interchangeably, they do not necessarily signify the same thing. While ODM manufacturing develops some or all of the product before manufacturing it for clients, OEMs build items based on designs supplied to them by customers. This blog will clarify the distinctions, OEM and ODM examples, advantages, and more of the two manufacturers’ categories.
Original Equipment Manufacturer OEM Definition
Original Equipment Manufacturers are companies that create goods in response to the needs of other companies. The item is sold to the ordering company, which subsequently markets it under the buyer’s brand. OEM has manufacturing capabilities, but it does not engage in R&D and solely produces products that meet the company’s specifications.
For instance, Apple created and developed the Apple iPhone before contracting Foxconn to manufacture it. As a result, the iPhone has a far higher level of product differentiation as only Apple and the manufacturer it has partnered with have access to the design.
Example Of an OEM Business
One typical instance is the partnership between an OEM that manufactures individual electronic components and a business-like Sony or Samsung that assembles those components to create HDTVs. Or a button manufacturer who produces Ralph Lauren branded fasteners with the monogram RL embossed on them.
Pros And Cons Of OEM
Pros
This kind of business partnership might be a terrific approach to launch a product and begin making money. By establishing an OEM agreement, you will be able to make a good that is expensive or time-consuming to produce, making it tough for customers or competitors to copy. By using an OEM, you can get entry to new markets, business sectors, and geographical areas.
- The product may be altered at the request of the customer. The design is under the buyer’s creative control. With a distinctive marketing strategy, it is simpler to pitch the clientele and stick out.
- With distinctive items, a brand can avoid fierce rivalry among the vendors.
- There is less chance of fabrication because copyrights make it difficult for thieves to produce copies of your stuff.
- The product is created with the highest level of accuracy feasible by the client’s request.
Cons
Providing a design brief to an OEM can be challenging. Miscommunication or gaps in understanding may require your team to visit the factory in person to clarify requirements.
This additional travel can consume time and resources, potentially impacting project timelines.
Additionally, during the manufacturing process, the OEM might propose alterations to the product. These changes may align with their manufacturing expertise but deviate from your original design brief.
Without direct involvement, your team won’t have the opportunity to provide input or feedback on these modifications.
- To create and produce a unique object, a substantial sum of money is needed.
- the challenging procedure and protracted manufacturing time.
Also Read: Lower the Cost of Your Carrier Shipping in 2022
Original Design Manufacturing ODM Definition
We’re familiar with OEM manufacturing. So, let’s examine more about ODM.
Original Design Manufacturers, commonly known as white-label or private-label products. In this instance, the client may make minor adjustments to an existing product design from the manufacturer to market it under their brand name. The use of new branding, color, or packaging is a few examples of alterations.
Car chargers are an example of an ODM product. On Amazon, you may search for car chargers and find products from several different manufacturers that are practically the same. While the products are produced using the same basic design, each is individually branded, colored, and packed to meet the needs of the consumer.
Example of an ODM business
A client who works in the education sector has identified a market gap. They approach an ODM with their proposal for a schoolbag that incorporates sections that cool drinks, food, and snacks while keeping other components entirely waterproof based on their understanding of the market.
After learning about the new schoolbag concept, the ODM schedules a meeting with the clients to go over the demand for this product in greater detail.
The customer describes the requirement for the product and what aspects of color and design might appeal to young kids during the meeting.
The ODM uses this market knowledge to create a school bag with compartments that are cooling water and stain-proof. Their design team works on the final designs’ style, textiles, and specifications.
Now, the ODM can either sell the product straight to the customer or the client, whom they can rebrand if they choose.
Pros and cons of ODM
Pros
ODMs can be more tempting to work with because they frequently have reduced minimum order quantities (commonly referred to as MOQs) requirements, especially for clients who wish to test out an idea. The cost to produce a new product is typically far lower than the cost of working with an OEM because the ODM has all the essential components to design, manufacture, and brand a product.
- Moulds won’t cost you anything. For specialized tools or moulds, your supplier must pay.
- ODM marketing typically moves more quickly than OEM.
- ODM reduces the time and cost of R&D.
- Connecting with a reputable ODM supplier can greatly reduce the risks of a duplicate product.
- A manufacturer doesn’t require a lot of capital or resources to produce a good. The ODM charges are quite affordable.
- ODM reduces the amount of time, energy, money, and resources required to develop new goods.
Cons
However, there are several drawbacks to ODM partnerships that may make clients hesitant to use an ODM. There are fewer chances to adapt, make changes, and regulate product needs because the client is only presenting an idea rather than the final product design. Because the factory has everything necessary to make the product on its own, without any additional input or assistance from the client, some people worry that their ideas might be stolen by the owner of an ODM product. Even if this might be the case, there are ways for clients to safeguard their concepts and for manufacturers to provide contracts that reassure new buyers.
- Selling ODM products makes it challenging to outperform the competition.
- ODM won’t let you alter many of their molds, so you can’t make the products specifically for your brand.
- The product’s intellectual property (IP) always belongs to the ODM.
The Main Keys Differences Between OEM And ODM
| Parameters of Comparison | ODM | OEM |
| Full form |
Original Design Manufacturing.
|
Original Equipment Manufacturing. |
| Meaning |
An ODM company is in charge of creating a product based on the requirements of another business. |
OEM designates a firm or enterprise in charge of creating, manufacturing, or selling the good to another firm. |
| Feature |
Create products according to client requirements.
|
independently creates items depending on requirements |
| Discovered |
ODM was first used in 1906.
|
OEM was first used in 1962. |
|
|
ODM is private labeling.
|
OEM is non-private labeling. |
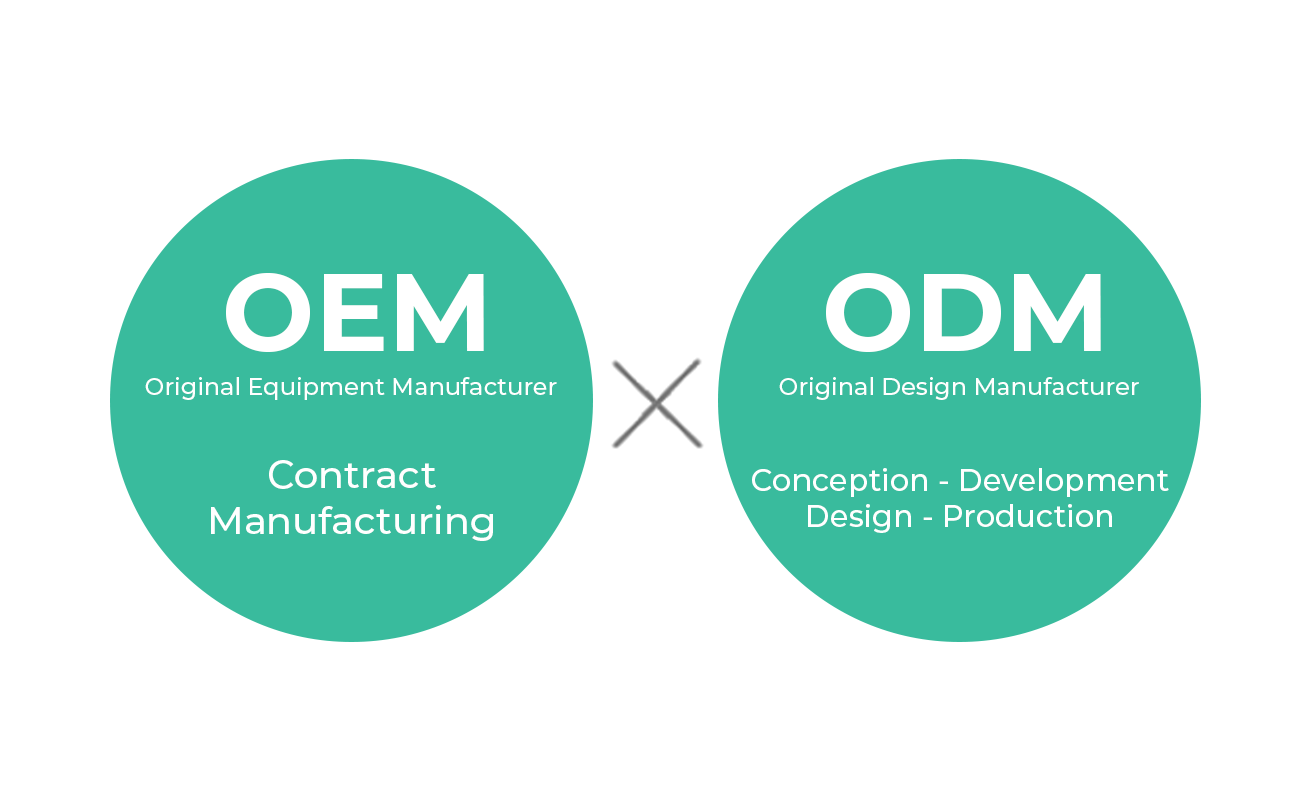
1. OEM vs. ODM:
– OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) refers to companies that design, manufacture, or sell products to other companies. They typically produce products based on their own specifications or those provided by the client.
– ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) firms, on the other hand, develop and manufacture products according to the specific requirements and designs provided by another company.
2. Private Labeling and ODM:
– While OEM often involves private labeling (where a product is sold under another company’s brand), ODM is not strictly limited to private labeling. ODM focuses more on customization and design modifications.
3. Customer Specifications:
– ODM creates items based on the exact specifications of the customer, tailoring the product to meet specific needs.
– OEM, in contrast, produces products according to its own specifications or those of the client.
4. Historical Origins:
– The term OEM was first used in 1962.
– ODM has a longer history, dating back to 1906.
5. Terminology:
– ODM stands for Original Design Manufacturing.
– OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturing.
Which Is Right for My Manufacturing Business?
You have the choice of sourcing your products through ODM or OEM. Each of them has advantages and disadvantages of its own. It will be quite difficult to answer which will be best for your business without knowing the goals and requirements of your company.
Companies that are not engaged in product marketing are drawn to the ODM approach. They seek to use well-known brands to market their goods. They simply use their particular IP address to pack the products.
For the major brands, high-quality customized items are produced using the OEM approach. It requires materials like a development budget, in-depth research, a practical marketing strategy, etc.
Therefore, firms that have the time and resources can choose OEM items.
You may learn more about inventory management by reading our previous posts.
Conclusion
The choice between OEM and ODM is directly influenced by the resources at hand. OEM is an option for businesses with sufficient funding for R&D. On the other hand, if time and resources are limited then ODM is the best fit.



Recent Comments