The Difference Between Backorder Vs Backlog
Supply Chain Management
LAST UPDATE: MAY 6, 2023
10 minutes reading
Supply chains are often overlooked or given little priority by online retailers. In a major way, a company’s prosperity rests on the efficiency of its supply chain. This requires giving careful consideration to your supply chain if you want your firm to succeed.
Supply chain optimization aims to eliminate the occurrence of any backorders. But what do you do when backorders begin to pile up? But suppose there was a backlog. How will you get through this temporary snag in order to keep giving your clients the best service possible?
Having a firm grasp of the distinction between a backorder vs backlog in supply chains, for instance, can influence strategic choices and ultimately strengthen a company. To better understand the difference between a backorder vs backlog, it is helpful to first define each term.
What Is a Backlog?
inventory backlog meaning a customer’s backlog of orders is the sum of all of their pending shipments in an online store. Many people make up this group because they have all placed orders for the product to be shipped. One buyer purchases an item on January 24 and specifies a shipping date of January 30. From January 24 through January 29, this purchase will be added to your pending orders.
What Is a Backorder?
The term “backorder” refers to an order that a business has not fulfilled because the product is temporarily out of stock. If the aforementioned order is not shipped by January 30, it will become a backorder. You’ll keep it in backorder until you’re ready to send it out to clients. Not only is the order still in your backlog, but so is the backlog item.
The Key Distinctions Between Backorder Vs Backlog
Having a backlog in your supply chain is actually beneficial, according to several supply chain experts, but having a backorder is detrimental to your company. Nonetheless, they have remarkably similar pronunciations. When put into context, what does backorder vs backlog mean?
Backlog in Supply Chains
Everything that has been ordered by clients but has not yet been sent out is considered part of your backlog. If on January 1, clients placed orders for teddy bears with a promised delivery date of February 1, such orders would be considered backlogged.
Backorder in Supply Chains
Every item that is delayed in transit is included on your list of backorders. Backorders are the things that you promised to deliver on February 1 but didn’t get out the door until February 2. (These items on backorder will still count towards your backlog.)
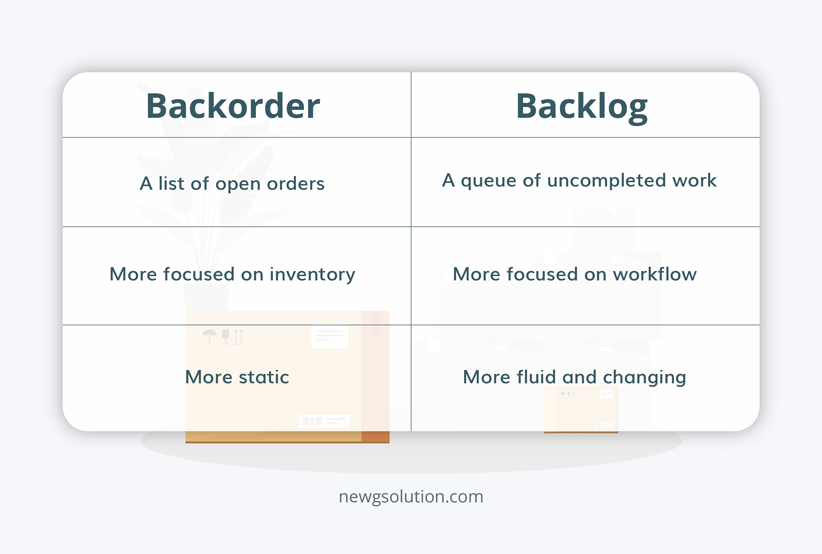
Here are a few key distinctions between backorder vs backlog:
- A backorder is a list of open orders; a backlog is a queue of uncompleted work
- A backorder is more focused on inventory, and the backlog is more focused on workflow
- A backorder is more static, whereas a backlog is more fluid and changing
Backlog Benefits
A backlog tactic might have a negative connotation in some settings. This is especially true when individuals experience “job overload.” In other words, they are overburdened with personal commitments and cannot catch a break.
In a similar manner, backlogs in supply chain management are often seen negatively. Inventory backlogs suggest that you are not keeping up with fulfillment, thus you run the danger of accepting orders you cannot fulfill.
However, backlogs can be advantageous when order and fulfillment operations are managed effectively. With well-managed inventory backlogs, you can maintain customer satisfaction, enhance your brand’s reputation, and earn money even while you are out of stock.
Satisfied Customers
This can significantly increase customer happiness and retention. Why? Because it allows consumers to make scheduled purchases and offers them something to anticipate.
Still, clients will only remain satisfied if you set clear expectations for when they will receive their item and then meet those expectations. A well-organized inventory backlog facilitates this action.
Good Reputation
In keeping with the preceding idea, your brand’s reputation can be bolstered by its capacity to meet consumer demand. Customers that are satisfied are more likely to become repeat customers and to spread the word about their great experience with your business.
72% of satisfied customers will tell 6 people about your brand if they had a positive encounter. If they had a negative experience, however (such as when you’re constantly sold out or their orders are late), they will tell even more people.
So, supposing your company is aware that the stock will be replenished within a specified time range. You can then begin selling these products on backorder.
If the replenishment date is within the timeframe in which you would typically ship a purchase made today, you can even sell the item as if it were in stock. (Be sure to create a backlog as you work.) Since you haven’t publicized your brand’s reliance on a backorder model, this strategy will give the impression that your company is well-organized.
The day the shipment arrives at your warehouse, then, staff a larger fulfillment team. Thus, you will be able to clear the inventory backlog as soon as the products return to your warehouse. And do so without doubling the workload of your team.
In addition, you will drastically reduce your holding costs by storing fewer items once the backlog is cleared.
Higher Revenue Flow
This uninterrupted revenue stream might have a significant impact on your bottom line. And it ensures you have a sufficient amount of working capital while you await your replenishment.
By accepting orders (even with delayed fulfillment), your company ensures it has adequate working capital on hand. For instance, you could utilize this money to expedite purchase order lead time by opting for speedier shipping methods in the event of a catastrophic failure. Or, you can engage more warehouse personnel to expedite order fulfillment.
Backorder Benefits
Just like backlogs, backorders typically have a poor rap among retail brands. The majority of business owners miss the benefits of selling on backorder. And they frequently fail to recognize the benefits it might have for their store.
In reality, though, backorders can help your business save money on storage space, acquire insight into consumer behavior, and enhance product value.
Cost savings on storage space
Brands selling on backorder require far less warehouse space than brands with a large quantity of stock on hand.
Consider: if you only routinely store a few products, you do not need a vast warehouse. Therefore, fewer things in stock result in lesser storage needs, reducing your storage expenditures by around $7.50 per square foot shed (to be exact).
In addition, having fewer storage requirements minimizes the cost of transporting your inventory. You only increase your total inventory costs by holding on to unsold items (like dead stock). And as a result, you reduce your gross profits.
However, by selling on backorder, your company can begin production or manufacture only after receiving consumer orders, so reducing its overhead expenses.
Gain knowledge about consumer behavior
Backorder sales provide unique information about product trends, consumer behavior, and more. You can simultaneously collect (and evaluate) the data around each order as you receive consumer orders for backordered goods.
Among other inventory KPIs, this data may comprise the inventory turnover ratio or days inventory outstanding (DOI). Additionally, it will emphasize things for which customers are willing to wait.
You can uncover purchasing patterns that will drive your replenishment cycles, safety stock, and other inventory management decisions with this information at your fingertips.
When reviewing your turnover ratio, for instance, you will have a better understanding of when, what, and how much you need to order to attain your economic order amount (EOQ).
Increase product value
Fear of missing out (FOMO) has expanded beyond social events and group activities in recent years. And it even affects the items we purchase. FOMO creates a sense of urgency and scarcity surrounding the purchase of a new product or possession of the newest device.
Consider the technology industry, for example. Apple is well-known for its backorder model for its most recent offerings. In 2017, when Apple unveiled the iPhone X, US customers were prepared to wait up to six weeks for their orders.
First, these backorders generated a great deal of iPhone-related buzz. However, they also raised the product’s value (and the customer’s perception of the product’s value). In other words, the strong demand for these goods on backorder caused people to desire them more than if they were constantly in stock.
Conclusion
Always keep in mind that improving your supply chain entails providing your customers with what they want when they want it. You will also want to spend as little money as possible to do this. By understanding the differences between backorder vs backlog Ensure that your consumers are aware of your lead times, and more importantly, ensure that you are aware of your own. Keep your backorders low and your backlog high, and you’ll be on your way to supply chain optimization.
With New G Solution, follow each stage of the order’s lifecycle, from creation to delivery and closing, to maintain control over its workflow. In addition, manage your customers’ balances and payments, as well as tax and commission computations.


Recent Comments