What is Reverse Logistics? How Does It Impact Your Inventory?
Supply Chain Management
LAST UPDATE: MAY 26, 2023
8 minutes reading
Successful supply chain firms employ reverse logistics to execute activities efficiently and increase value for their end consumers. Supply chain professionals can use their newfound knowledge of reverse logistics to cut costs and maintain efficiency by familiarizing themselves with the many types of reverse logistics and the difficulties associated with their coordination and administration.
What is Reverse Logistics?
In the context of the supply chain, “reverse logistics” describes the process by which products are returned from consumers to wholesalers or manufacturers.
Offering returns to customers is helpful for the company, whether they are returning products they no longer need, the product has reached the end of its life cycle, or the product is damaged or faulty.
This method is applicable not only when products are being discarded or recycled, but also when the final consumer is responsible for the product’s upcycling, disposal, or even resale.
When Is Reverse Logistics Used?
As items reach their final destination, the organization employs reverse logistics to transport them back through the supply chain to the original seller and, in some cases, the original suppliers. The objective is to sell or otherwise get rid of the product so that it can be put to good use again. Because of the rise of online shopping, refunds are now a frequent practice that totals about a trillion dollars annually.
Value recovery and client retention are two main goals of reverse logistics. The return rate for in-store sales is under 10%, but it’s at least 30% for internet orders. Businesses that are astute as they employ reverse logistics to increase client retention and repeat sales while reducing the costs associated with returns.
Reverse Logistics vs. Traditional Logistics
The traditional production process begins with the suppliers and continues on to the manufacturer or distributor. The products are then distributed to shops and end users. Management of the flow of goods in the opposite way, from the consumer back into the supply chain, is known as reverse logistics.
In addition to adapting quickly to new circumstances, efficient supply chains are also capable of meeting some of the demands placed on them by reverse logistic. This backward procedure can either send goods back to the source or to the previous link in the supply chain. Products that are returned to sellers can be put back on the market or discounted (like liquidators).
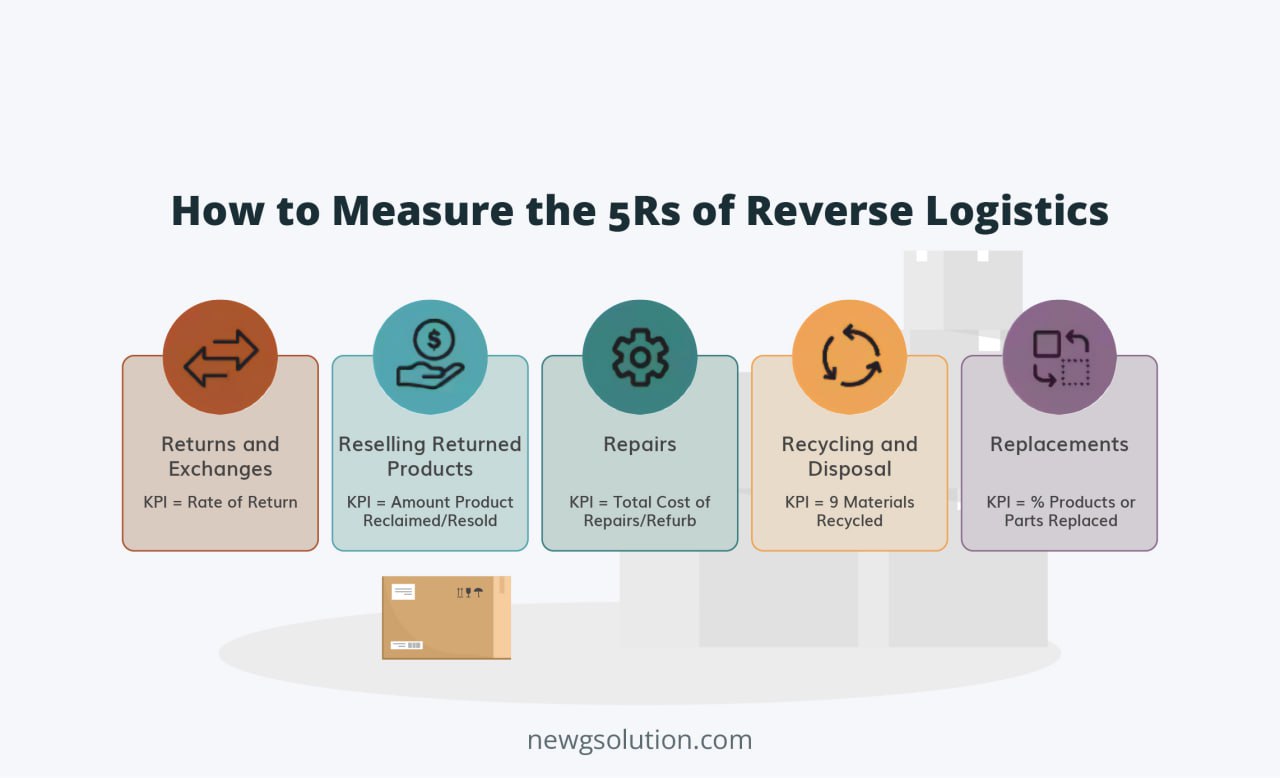
What Are the 5Rs of Reverse Logistics?
What Are the Types of Reverse Logistics?
1- Managing Returns
Customer loyalty and positive perception of a company’s brand can be bolstered by improving the returns handling process, the most prevalent type of reverse logistic.
2- Procedures and guidelines for returns
All exchanges and refunds must comply with this policy, which must be applied uniformly by both consumers and staff. Having these rules readily available to customers is a good business practice.
3- Reprocessing, also known as refurbishing
Organizations and stores can avoid losing money (or making no money) on returned products by putting them through a reconditioning process.
4- Methods for controlling packaging
Companies that have implemented a packaging management system are better equipped to recycle and repurpose returned packages, thereby lowering their environmental impact and saving money.
5- Products that were not sold
The practice of returning unsold products from customers or distribution centers to producers is known as “reverse logistics” and is typically the consequence of delivery refusal, low sales, or other circumstances.
6- Arrival at the end of the product’s useful life
When a product has reached the end of its useful life, it should be returned to the maker so that they may arrange for proper environmental disposal.
7- Inability to Provide
Delivery failure typically results in products being sent back to a fulfillment center, where they can be sent back to the manufacturer; however, well-run businesses can handle this situation by identifying the cause, fixing it, and resending the package.
8- Machinery for hire
After a specified period of time, rented or leased items are returned to the maker for processing, refurbishment, or recycling.
9- Adjustments and upkeep
Many types of consumer electronics (including laptops) allow for the device to be returned for service under warranty.
Importance of Reverse Logistic
Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer or another point in the supply chain for reuse, repair, recycling, or disposal. Reverse logistic is important for several reasons:
- Improves customer experience and satisfaction by offering easy returns, refunds, and exchanges. This can encourage repeat business and loyalty.
- Reduces waste and costs by recovering value from returned products. This can improve the bottom line and profitability of the organization.
- Reduces the environmental impact of the organization by minimizing landfill waste, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource consumption. This can enhance the sustainability and social responsibility of the organization.
- Protects the health and safety of customers and society by recalling defective or hazardous products. This can improve the reputation and trustworthiness of the organization.
- Closes the loop on the product life cycle by ensuring that products are properly disposed of or reintegrated into new products. This can foster innovation and competitiveness in the market.
In short, Reverse logistics is a vital part of any supply chain management strategy that aims to optimize customer service, operational efficiency, environmental performance, and financial results.
Reverse Logistics Process
Reverse logistic is the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer or another point in the supply chain for reuse, repair, recycling, or disposal. The reverse logistics process typically involves the following steps:
- The customer initiates the return, following the seller’s requirements for mailing or physically returning the item to the seller or manufacturer.
- The item is transported to a returns processing facility, where it is inspected, cleaned, or repaired if necessary.
- The item is re-sold, recycled, re-used, or landfilled, depending on its condition and value. The seller may also recover parts or materials from the item for future use.
- The customer is refunded the cost of the item or credited with a replacement or exchange.
overall, The reverse logistics process can vary across different industries and products, depending on factors such as customer expectations, product quality, environmental regulations, and economic incentives. Reverse logistic requires careful planning and coordination among various stakeholders in order to optimize customer service, operational efficiency, and financial performance.
The Stages Of Reverse Logistics
Process The Return
When customers initiate a return, the organization must then initiate the return process and put its standard operating procedure in motion. Every company that deals with returns need to have an organized method of initiating returns.
Determine The Return Category
Upon return, products need to be inspected in order to determine where they should be placed next in the process. Once a product is returned there are a few options for the next steps. It may need to undergo refurbishment, recycling, or be prepped for resale to fill another order.
Move Products to Reduce Waste
Continuously keeping returned products in motion can help to reduce the amount of waste produced when products sit for lengthy periods. Items due for repairs should be moved quickly to the repair department so that they are not left in the balance.
Execute The Repair Process
Items relocated to the repair department should be dealt with in a timely fashion so that any necessary end-of-life arrangements can be made. Repairable items should be repaired quickly and reinstated into the organization’s inventory or disposed of if they are irreparable.
Recycle Items That Cannot Be Repaired or Resold
If it can’t be fixed or parted out, it must be disposed of in the correct fashion. Organizations must do their due diligence when it comes to recycling and disposing of items that cannot be repaired. This means taking environmental sustainability into account and addressing issues that result from wasted products.
Reasons Why Reverse Logistics Should Be Optimized
When reverse logistics are optimized, not only are there financial benefits but there are also positive effects on the environment and company culture. Reducing waste and improving client retention can be achieved by streamlining post-delivery operations.
One benefit of properly implemented reverse logistic is the product information gathered through post-delivery customer interaction. Information can help a business enhance its supply chain, which in turn benefits its products and the service it gives to customers.
Improved supply chain visibility, a result of optimized reverse logistics, has many positive effects, including:
- Eliminating Extra Expenses
- Enhanced happiness amongst the product’s target audience
- Increased consumer loyalty
- improved efficiency and speed
- Loss mitigation
- Enhanced consumer opinion of the brand
- Less garbage and more longevity
How Do Reverse Logistics Impact Supply Chain Management?
Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from their typical final destination for the purpose of capturing value, or proper disposal. It can also include remanufacturing and refurbishing activities. Reverse logistic can have a significant impact on supply chain management, as it can help improve customer satisfaction, reduce waste and environmental impact, and recover value from returned products.
However, reverse logistic can also increase supply chain costs, such as transportation, storage, inspection, and disposal costs. Therefore, reverse logistics requires careful planning and execution to balance the benefits and challenges it poses for the supply chain management.
Conclusion,
Reverse logistics is a vital aspect of supply chain management that deals with the movement of goods from the end consumer back to the manufacturer or distributor for various purposes, such as returns, repairs, recycling, or disposal. Reverse logistics can have a significant impact on inventory management, as it can help reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, recover value, and enhance sustainability.
However, reverse logistic also poses some challenges for inventory management, such as increased complexity, uncertainty, variability, and quality issues. Therefore, reverse logistic requires effective planning and execution to optimize inventory levels and performance.




Recent Comments